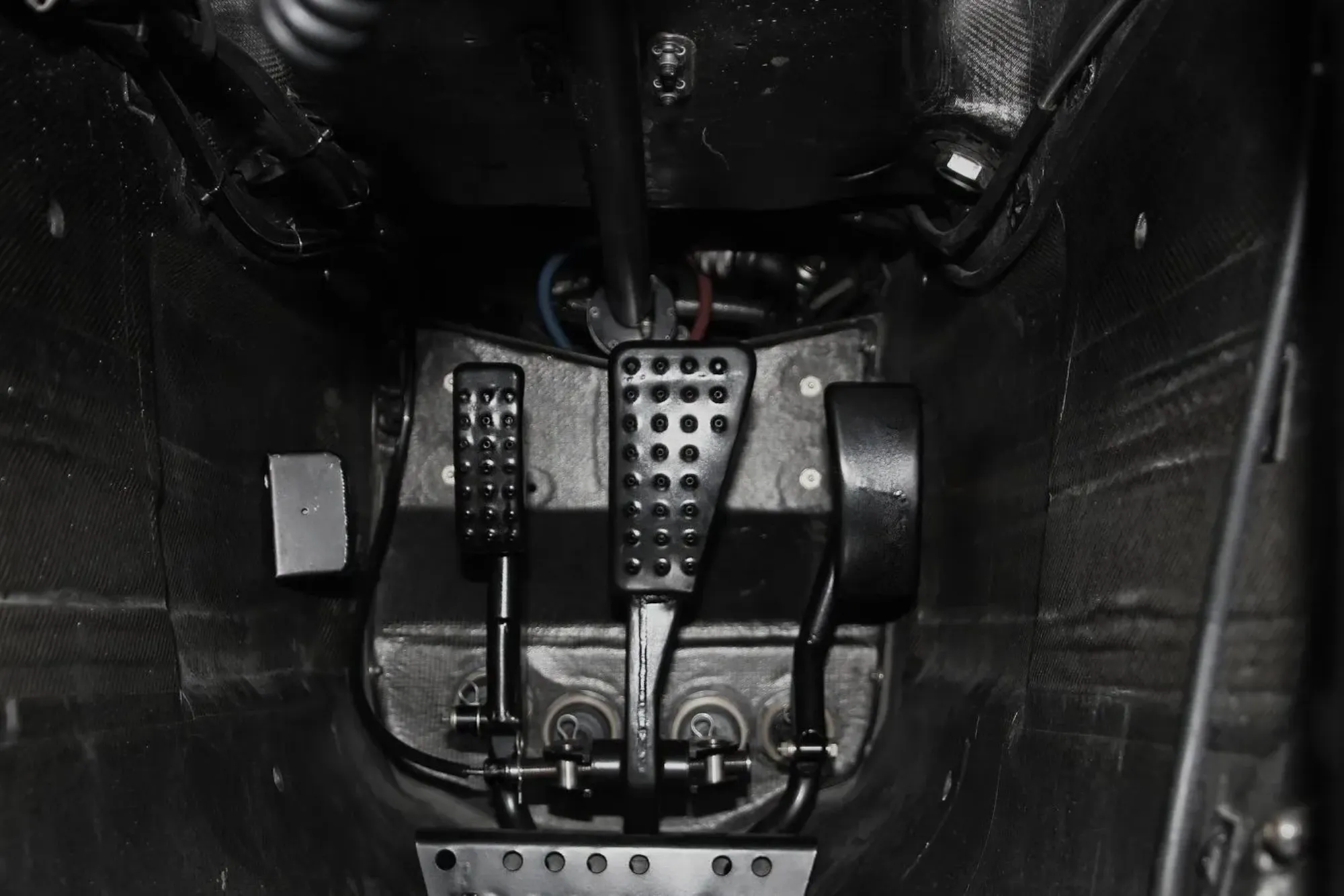
A car with four pedals is an uncommon sight on the roads today. Typically, most vehicles come with three pedals: the clutch, brake, and accelerator. However, a car with four pedals may seem unusual but is not impossible. This article will delve into the possibility, types, and functioning of cars that could potentially have four pedals. We will explore the mechanics, driving experience, and even discuss how this could affect the future of automotive technology.
What Are the Common Pedals in a Car?
In most traditional cars, particularly manual transmission vehicles, there are three main pedals. Each pedal has a distinct function:
- Clutch: Used in manual cars to disengage the engine from the wheels to shift gears.
- Brake: Allows the driver to slow down or stop the vehicle.
- Accelerator: Used to increase the speed of the car.
These three pedals are common in manual and some automatic cars. However, the idea of a fourth pedal may seem confusing or surprising. But what could this fourth pedal be for, and how would it work?
What Is a Car with Four Pedals?
A car with four pedals is generally seen in specialized vehicles. Some vehicles might be equipped with additional features or systems that require an extra pedal. The fourth pedal could serve various purposes, depending on the car’s design and technology. Let’s look at the possible scenarios in which a car could have four pedals.
The Fourth Pedal in a Hybrid or Electric Vehicle
Some advanced hybrid or electric vehicles may feature a fourth pedal for regenerative braking or other unique functions. This additional pedal could provide the driver with more control over the car’s energy recovery system, allowing them to manage braking efficiency or even energy distribution in certain driving modes. Regenerative braking, which recovers energy when braking, is a key feature in electric vehicles, and the fourth pedal could allow the driver to modulate this system.
The Fourth Pedal in Performance or Racing Cars
In performance vehicles or racing cars, a fourth pedal might be used to control an additional system, such as a boost control system. In racing scenarios, drivers need more control over the car’s performance, and the extra pedal can be used to manage functions like boost pressure, fuel mixture, or even suspension settings.
Custom and Experimental Cars
Some experimental or custom-built cars may have a fourth pedal as part of their design. Engineers may develop these systems to test new technologies or improve vehicle performance. These cars are typically not for mass production but may appear in concept vehicles or as prototypes for testing.
How Does a Car with Four Pedals Work?
To understand how a car with four pedals functions, it’s essential to explore the mechanics behind it. In most cases, the four pedals would work in conjunction with each other, allowing the driver to control the vehicle more precisely. Here’s a breakdown of how each pedal might function:
Clutch Pedal
The clutch pedal in a manual car disconnects the engine from the transmission, enabling the driver to shift gears smoothly. This pedal remains a critical part of any manual car, even if there are additional pedals for other functions.
Brake Pedal
The brake pedal controls the vehicle’s ability to slow down or stop. In most cars, this is one of the most critical pedals for safe driving.
Accelerator Pedal
The accelerator controls the speed of the car. In a car with four pedals, this pedal functions the same way as it would in a traditional vehicle.
Fourth Pedal: Regenerative Braking or Custom Function
The fourth pedal could serve multiple functions. For instance, in electric or hybrid vehicles, it might control regenerative braking, helping the car recover energy during deceleration. Alternatively, in a performance car, it might control an advanced feature like a boost system, turbocharging, or suspension adjustments.
The Benefits of a Car with Four Pedals

While most cars use only three pedals, the introduction of a fourth pedal could provide several advantages, especially for drivers seeking more control and efficiency. Some benefits include:
Increased Control and Precision
A fourth pedal can provide drivers with more options to manage vehicle performance. For instance, the driver can adjust the regenerative braking system or boost settings to optimize driving efficiency, especially in electric or hybrid cars. This additional control could also enhance safety by providing better braking responses.
Enhanced Energy Efficiency
For hybrid and electric vehicles, a fourth pedal that controls regenerative braking allows the vehicle to recover energy when slowing down. This improves fuel efficiency and extends the driving range of electric vehicles. By modulating how much energy is recovered, the driver can further optimize the vehicle’s energy usage.
Improved Performance for Racing or Custom Cars
In performance vehicles, the fourth pedal can help the driver adjust critical systems like turbo boost or suspension settings, making the car more adaptable to different driving conditions. This could lead to better lap times and improved overall handling on the track.
Potential Drawbacks of a Car with Four Pedals
While there are several benefits to a car with four pedals, there are also some challenges and potential drawbacks:
Complexity and Learning Curve
For drivers used to traditional vehicles with three pedals, the addition of a fourth pedal can complicate the driving experience. New drivers may find it difficult to adjust to this added complexity, and there may be a learning curve to understand how the fourth pedal functions.
Increased Maintenance and Repairs
With the addition of another pedal and system, the vehicle’s complexity increases. This could lead to higher maintenance costs, as more components need to be maintained and repaired. Additionally, specialized training may be required for mechanics to handle these systems effectively.
Limited Availability
Cars with four pedals are not yet common, and finding such vehicles could be a challenge. These cars are typically seen in specialized markets, such as performance vehicles, racing cars, or electric vehicles with unique features. As such, the options for consumers are limited.
Table: Pedals in Different Types of Cars
| Car Type | Pedals in Use | Function |
|---|---|---|
| Manual Transmission | 3 Pedals (Clutch, Brake, Accelerator) | Standard pedals for gear shifting, braking, and acceleration |
| Hybrid or Electric | 3 Pedals + Regenerative Brake Pedal | Extra pedal for managing energy recovery through regenerative braking |
| Performance Cars | 4 Pedals (Including Boost/Suspension) | Extra pedal to control performance features such as boost pressure, fuel mixture, or suspension |
| Experimental Cars | Varies (Up to 4 Pedals) | Custom pedals for testing new technologies or advanced vehicle systems |
FAQs About Cars with Four Pedals
1. What is the purpose of the fourth pedal in a car?
The fourth pedal in a car can serve various functions depending on the type of vehicle. It may control regenerative braking in hybrid or electric cars, or it could be used to adjust performance systems like boost control in racing cars.
2. Are cars with four pedals common?
No, cars with four pedals are relatively rare. They are typically found in specialized vehicles, such as electric cars with advanced energy recovery systems or performance cars used for racing.
3. How does regenerative braking work with the fourth pedal?
In electric or hybrid cars, the fourth pedal could be used to control the regenerative braking system, allowing the driver to adjust how much energy is recovered during braking, which can improve efficiency and range.
4. Can I drive a car with four pedals if I am used to three pedals?
It may take some time to adjust to a car with four pedals, as it adds complexity to the driving experience. However, with practice, drivers can learn how to operate the additional pedal effectively.
5. What are the benefits of a fourth pedal in performance cars?
In performance cars, the fourth pedal can control features like turbo boost, fuel mixture, or suspension settings, allowing drivers to fine-tune the car’s performance for different driving conditions.